LED vs LCD vs Neon: Digital Signage Technology Comparison
Choosing between LED vs LCD digital signage, or even traditional neon, requires understanding fundamental technology differences. Each display technology offers distinct advantages in brightness, resolution, viewing angles, and installation flexibility. This comparison examines pixel pitch calculations, brightness specifications, and real-world performance data to help you select the right technology for your application.
What's the Real Difference Between LED and LCD for Signage?
LED emits light per pixel; LCD uses backlit liquid crystals with bezels. This fundamental distinction drives every other performance metric.
Direct-view LED (dvLED) displays use individual light-emitting diodes arranged in a matrix. Each diode produces its own light, eliminating the need for backlighting. Modern indoor LED configurations achieve pixel pitches from 0.9 mm to 4 mm, while outdoor variants typically range from 2.5 mm to 16 mm.
LCD technology sandwiches liquid crystals between polarising filters, requiring constant backlighting—typically edge-lit or direct-lit LED arrays behind the panel. The liquid crystals twist to control light passage, creating the image. This architecture necessitates structural support, creating visible seams in multi-panel installations.
When is LED the Better Choice?
LED suits high-brightness, large, outdoor and bezel-free installations. Consider these performance advantages:
Brightness: 800–10,000 nits (outdoor models reach 6,000+ nits standard).
Seamless scaling: No bezels between cabinet modules.
Viewing angles: 160° horizontal/vertical with minimal colour shift.
Lifespan: 100,000+ hours at 50% brightness (LM-80 verified).
Modular design: Hot-swappable components minimise downtime.
A west-facing installation requires 5,000+ nits to remain readable during summer afternoons. Only outdoor LED displays deliver this brightness while maintaining colour accuracy at extreme viewing angles.
When is LCD the Better Choice?
LCD excels at close-view, high-resolution applications where detail matters. Key advantages include:
Close viewing: Sharp text and graphics from 1 metre.
Standardised sizes: 43", 55", 65", 75", 86" with VESA mounting.
Proven technology: Mature manufacturing yields consistent quality.
Reception areas and wayfinding applications often favour LCD when viewers stand within 3 metres. The higher pixel density renders fine text and detailed graphics that would require sub-1mm LED pitch at a higher investment.
How Does Neon Compare to LED and LCD?
Neon offers unique aesthetics but faces practical limitations versus modern alternatives. Traditional glass neon remains unmatched for certain artistic applications.
Glass neon tubes bent to shape and filled with noble gases create a distinctive warm glow with omnidirectional light emission. The subtle colour variations and authentic character suit heritage shopfronts and hospitality venues seeking nostalgic appeal. Technical characteristics include:
Colour temperature: 2700K–6500K depending on gas mixture
Beam angle: 360° omnidirectional emission
Dimming: Limited range without colour shift
Custom shapes: Infinite possibilities with skilled glass bending
Operating voltage: 3–15 kV requires specialist transformers
Understanding Brightness Specifications
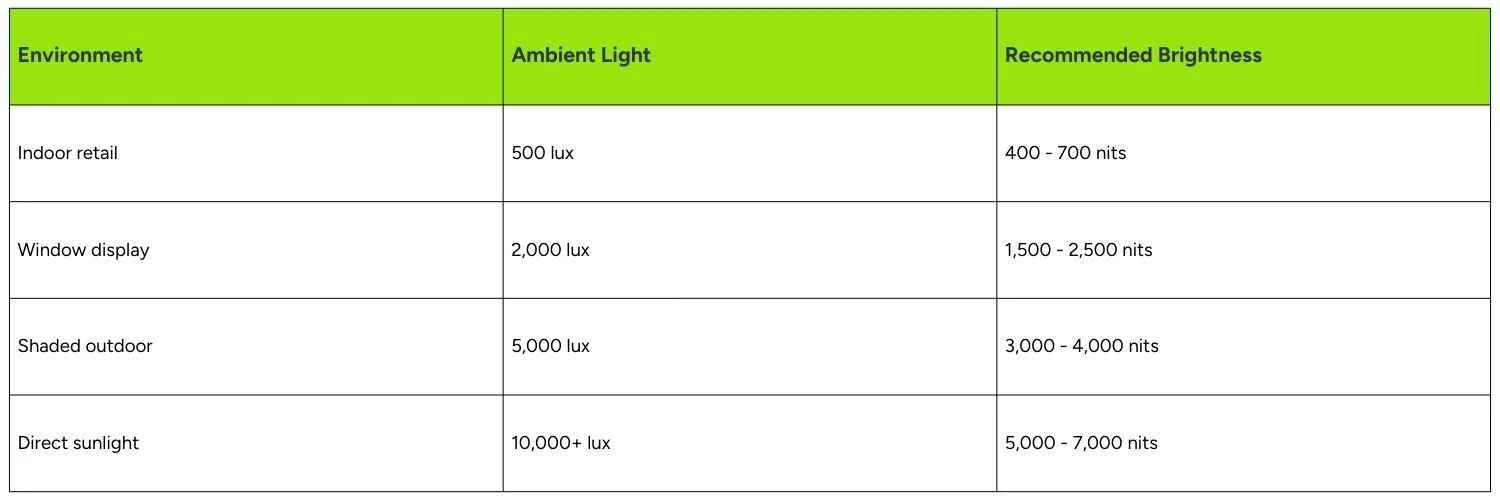
Brightness determines visibility in ambient light conditions. Measured in nits (cd/m²), requirements vary dramatically by application.
Indoor environments typically need 400–800 nits for comfortable viewing. Outdoor applications demand significantly more to combat sunlight:
What Pixel Pitch Suits My Viewing Distance?
Minimum viewing distance ≈ pixel pitch (mm) × 1000. This calculation ensures pixels blend into smooth images.
Understanding pixel pitch helps specify the right resolution for your application:
Environmental Durability and Protection
IP ratings define resistance to dust and moisture ingress. Australian conditions demand robust engineering across all climates.
Understanding IP Ratings
IP65: Dust-tight, protected against water jets
IP66: Dust-tight, protected against powerful water jets
IP54: Dust-protected, protected against splashing water
IP20: Indoor use only, no moisture protection
LED cabinets achieve IP65 through sealed module design, conformal-coated PCBs, and breathable membranes that equalise pressure while blocking moisture. Front-service designs allow maintenance without rear access, ideal for wall-mounted installations.
LCD technology requires separate protective enclosures for outdoor use, adding complexity:
Modular Design vs Panel Arrays
LED's modular architecture enables scalability and redundancy. LCD relies on discrete panel arrangements.
LED displays comprise multiple cabinets (typically 500mm × 500mm or 500mm × 1000mm), each containing removable modules. This architecture offers:
Scalability: Build any size or aspect ratio
Redundancy: One module failure doesn't stop the display
Serviceability: Hot-swap modules in minutes
Transportation: Ship in manageable components
LCD video walls use discrete panels in fixed sizes. Matrix processors handle signal distribution, but bezels remain visible even with ultra-narrow (0.88mm) options. Calibration across panels requires ongoing adjustment to maintain uniformity.
Which Technology Best Suits Your Application?
Match technology to specific requirements rather than following trends. Each solution excels in particular scenarios.
Application-Specific Recommendations
Retail Shopfront: LED delivers 24/7 visibility with 5,000+ nits for daylight competition. Choose 2.5–4mm pitch for typical pedestrian viewing distances.
Corporate Boardroom: Fine-pitch LED (1.2–1.5mm) creates seamless video walls without bezels. LCD works for single-screen presentations under 100".
Quick Service Restaurant Menu: High-brightness LCD (2,000+ nits) for drive-through visibility. LED if incorporating creative shapes or sizes beyond standard panels.
Transportation Hub: LED for main concourse displays visible from 20+ metres. LCD for gate-area information viewed at close range.
Entertainment Venue: LED stage screens handle touring productions' varied content. LCD for static lobby displays and wayfinding.
Architectural Features: Transparent or mesh LED preserves building aesthetics. LED-neon for accent lighting without structural modification.
Engineering Your Optimal Display Solution
Selecting between LED vs LCD digital signage demands careful evaluation of technical specifications against application requirements. LED dominates where brightness, scale, or creative freedom matter most. LCD wins on resolution density and standardisation for close-viewing applications.
Consider viewing distance, ambient light conditions, content type, and architectural constraints when specifying display technology. Pixel pitch calculations, brightness requirements, and environmental factors all influence the optimal choice.
Request a technical consultation — Our engineering team will analyse your requirements and recommend the optimal display technology with detailed specifications, 3D visualisations, and performance modelling.